- Aquatic Ecosystems
What is a Lotic System?
A lotic system includes all flowing inland bodies such as creeks, rivers, streams, and so on. The ecology of flowing water is unique in many ways and is often shaped by the nature and behavior of the flowing water. A river, for example, is a flowing water body, usually unidirectional, with a source and an end. It is usually in constant physical change. At the source of the river, it is narrower in size, cold, fast-flowing, and rich in oxygen. Down to the end, it is usually wide in size, less oxygen, slow-moving, and warmer. That means lifeforms in a lotic system is not the same, as it depends on the following:
1. The nature and behavior of flowing water
- The chemical makeup such as oxygen, pH, and alkalinity
- The temperature of the water, depth of the water and how much sunlight can penetrate it, and so on
- The velocity of the water
- The stage of the river in its course. Flowing water at its source tend to flow very fast, whiles water at its end tend to flow very slowly with a lot of nutrients and particle deposition
- The topography of the land (slopes, highlands, and lowlands)
2. The adaptation of its living organisms
With the above picture of flowing water in mind, how are living organisms (plants and animals) adapted to survive in these flowing water bodies?
- Organisms in these waters have suckers and hooks that help them stick to the water-bed, rocks, or plants.
- Some of them also have a streamlined body that helps them swim against water currents.
- Plants such as diatoms, moss, and sponges attach themselves firmly with the substratum.
3. The living structure along the flowing water
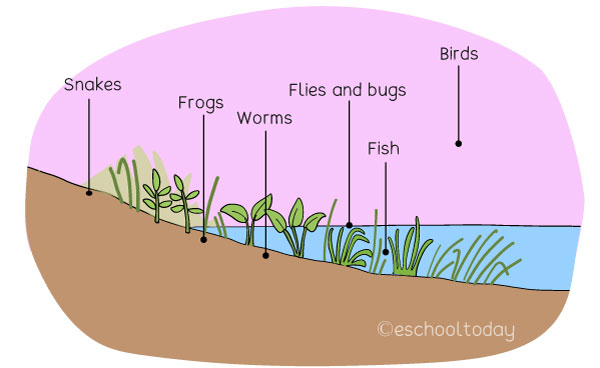
Some other plants and animals do not live in the water but are a part of the ecosystem that exists in that flowing water. Small plants, insects, frogs, birds, and other animals that feed off the plants from the flowing water, in turn, provide organic material for life forms in the water. The trees provide shelter for the birds and animals and also provide shade for slowing down evaporation. Some plants and their root systems also filter the water from pollutants.
