- Soils
What is Soil Conservation?
From the pages earlier, we learned about the role of soils and how essential they are for life on Earth. Unfortunately, soils are under threat in many ways, from excessive farming practices, use of chemicals during agricultural practices, water, land, and air pollution, erosion, and so on. These activities upset the natural function of soils and affect many ecosystems that depend on them for survival.
That is why soil conservation is important. It is the actions we can take or things we can apply to our use of soils and lands to ensure their sustained health and quality.
Here are a few:
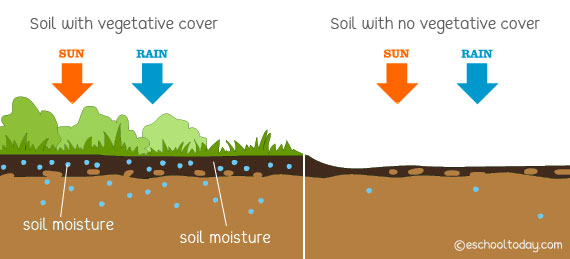
Planting vegetative cover:
The root systems of vegetative cover hold soils in place and prevent wind and water erosion. It also ensures its supply of organic matter from dead leaves and the dropping of animal waste. The vegetative cover also shelters the soils from excessive heat from the sun. It helps to reduce evaporation and retain soil moisture needed for the breakdown of organic matter.
Careful waste disposal and management:
When we recycle more and compost our food waste, we reduce the number of contaminants that we introduce to soils. We also give back to the land, rich humus from composts that we do. This is why we need to manage our waste well to ensure that our soils are alive and healthy.
Farming Practices:
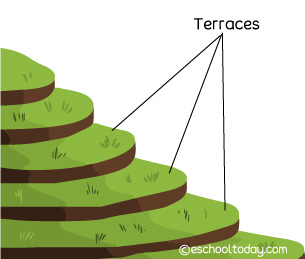
No-till farming, terrace, and contour farming are all great ways to conserve soil quality. Regarding no-tilling, crops are allowed to stay after the harvest season, to shed off naturally, thereby holding the soil together and sheltering the soils from wind and water action. Terrace and contour farms take into account the slope of the land to reduce run-off after the rains. In many places, windbreaks, usually composed of trees or shrubs planted along specific distances in farms are effective ways of controlling wind erosion.
