- Ecosystems
What is The Carbon Cycle?
The carbon cycle is important to all ecosystems, and ultimately life on Earth. The carbon cycle is critical to the food chain.
Living tissue contains carbon because it contains proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. The carbon in these (living or dead) tissues is recycled in various processes.
Let’s see how this cycle works using the simple sketch below:
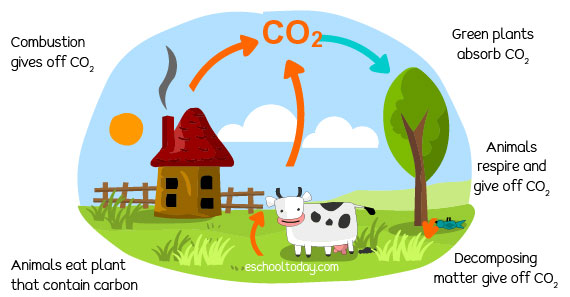
Human activities like heating homes and cars burning fuels (combustion) give off carbon into the atmosphere. During respiration, animals also introduce carbon into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is absorbed by green plants (producers) to make food in photosynthesis. When animals feed on green plants, they pass on carbon compounds to other animals in the upper levels of their food chains. Animals give off carbon dioxide into the atmosphere during respiration.
Carbon dioxide is also given off when plants and animals die. This occurs when decomposers (bacteria and fungi) break down dead plants and animals (decomposition) and release the carbon compounds stored in them.
Very often, energy trapped in the dead materials becomes fossil fuels that are used for combustion again at a later time.
