- Drugs Abuse
How do drug use and abuse affect the brain?
The brain is a vital organ in our bodies. It is the place where every information in our body is sent for processing. It is also the hub that connects all other sensory organs.
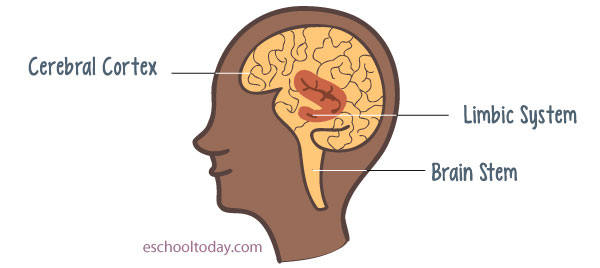
Three areas of the brain that drugs can affect are The Brain Stem, The Cerebral Cortex, and The Limbic System.
The Brain Stem is the part of the brain that controls vital functions of life such as breathing, sleeping, and heart rate.
The Cerebral Cortex functions in two ways, firstly it controls information from our senses such as sight, hearing, and tasting. Another part controls problem-solving skills, thinking, decision making, and so on.
The Limbic System regulates our ability to feel pleasure. It is the reward circuit that registers pleasure and causes us to pursue more pleasure. In simple terms, it reminds us of things that feel great to us and behaviors that bring that feeling. It controls our emotions, feelings, and moods.
All three parts work together in harmony. Drug use interferes with the normal way in which our nerves communicate with our brains. Prolonged drug use disrupts the natural balance of the brain’s functions.
For example when a person takes a drug for pleasure, the chemicals in the limbic system surge. The brain remembers that. After the pleasure effect is gone, the brain remembers that pleasure and wants more. That feeling to go for more is very strong and the user often has no control of the situation because the brain has hijacked the person’s checks and balances mechanism.
