- Wildfires
Introduction to wildfires
Out of the many natural disasters we have, wildfires would be the one that is very common, very difficult to fight, and maybe the most dangerous.
What is Fire?
Simple, it is the visible part of combustion. Combustion is a chemical reaction of three things: Heat, Fuel, and Oxygen. These three ingredients must be present before a fire can be started and maintained.
Let us consider the fire triangle below.
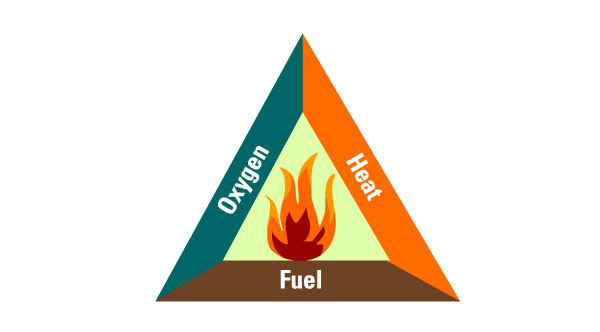
For the fire triangle to stand, all three ingredients must be present. If the heat is not enough, or the fuel runs out, or the oxygen runs out, the fire will be out.
Oxygen:
It is a gas found in the air. The air we breathe contains about 21% oxygen. Only 16% is all that is needed to produce fire. When fuel burns, it reacts with oxygen from the surrounding air. This chemical reaction releases heat and other products such as gases, smoke, and particles. This process is known as oxidation. It explains why some smoke can be dangerous because depending on what is burning, the gases produced can be very deadly.
Fuel:
Fuel is any combustible material. It can be gas, liquids, or solids. Some examples of fuels that are solids include wood, dry leaves, and paper. Some examples of fuels that are liquids include petrol and turpentine. Examples of gas fuels include LPG Gas. Fuel with less moisture tends to burn faster than fuels with high moisture.
Heat:
Heat is thermal energy. You may not see it but can feel it. The extreme heat of about 617°F will start a fire in the presence of fuel and oxygen. Heat eliminates moisture from any nearby fuel, warms the air around, and prepares the fire path to accept the fire and make it burn with ease.
