- Air Pollution
Indoor Air Pollution
‘Indoor air’ is the air within a building such as your home, classroom, office, shopping center, hospital, or gym. We say ‘Indoor Air Pollution’ if the indoor air is contaminated by smoke, chemicals, smells, or particles.
Unlike outdoor air pollution, the effect of indoor air pollution is health-related and less of an environmental issue. In colder regions, building and heating methods make use of airtight spaces, less ventilation, and energy-efficient heating. Sometimes, synthetic building materials smells from household care products, and furnishing chemicals can all be trapped indoors. As less fresh air gets indoors, the concentration of pollutants such as pollen, tobacco smoke, mold, pesticides, radon, asbestos, and carbon monoxide trapped inside the building increases, and people breathe that in.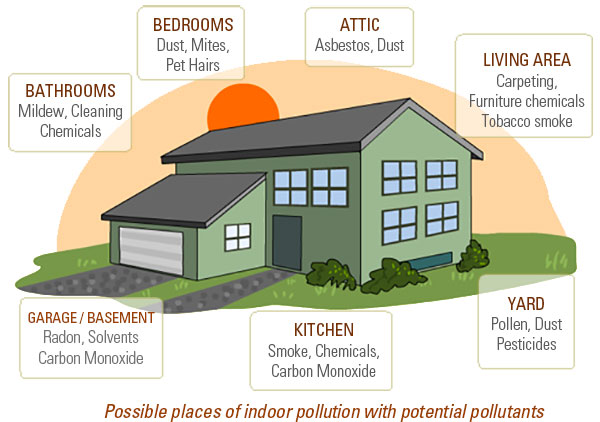
Did you know:
- Around 3 billion people cook and heat their homes using open fires and leaky stoves, and burning biomass (wood, animal dung, and crop waste) and coal.
- Nearly 2 million people die prematurely from illness attributable to indoor air pollution from household solid fuel use.
- Nearly 50% of pneumonia deaths among children under five are due to particulate matter inhaled from indoor air pollution.
- More than 1 million people a year die from chronic obstructive respiratory disease (COPD) that develop due to exposure to such indoor air pollution.
- Both women and men exposed to heavy indoor smoke are 2-3 times more likely to develop COPDSource: WHO: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs292/en/
Common indoor air pollutants include:
- Tobacco smoke:
It is smoke from burning cigarettes or smoke exhaled by people smoking. - Biological Pollutants:
These include allergens such as pollen from plants, hair from pets, fungi, and some bacteria. - Radon:
It is a gas that is naturally emitted from the ground. Radon can be trapped in basements of buildings and homes. The gas is known to cause cancer after exposure over a period. - Carbon Monoxide:
It is a poisonous gas with no color or smell. Carbon monoxide is produced when fuels such as gas, oil, coal, or wood do not fully burn.
