- Nutrients in food
Carbohydrates in food
Carbohydrates essentially give the body cells the energy they need every day. There are three categories of carbohydrates. The illustration below shows the three categories.
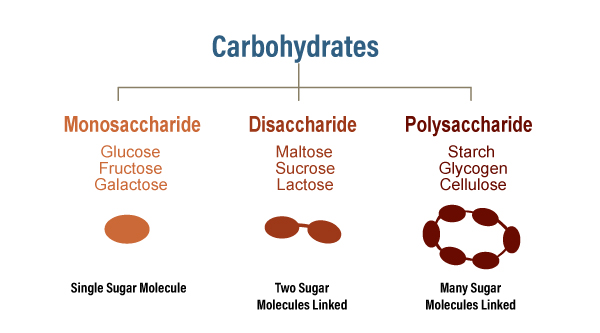
Monosaccharides
Carbohydrates in this group are in a simple form and include single sugars that are easily absorbed into the bloodstream. Saccharide simply means sugar. They come from foods like honey, fruit juices, and some vegetables and are a source of quick, instant energy.
Disaccharides
Carbohydrates in this group are naturally occurring sugars. They are chemically composed of two sugars linked together and need certain enzymes to break them up to release the sugars. Maltose, sucrose, and lactose are in this group and foods such as milk or table sugar.
Polysaccharides
These are more complex carbohydrates. They are made of many simple sugars linked together. Starch and cellulose are examples of polysaccharides found in carbohydrates. They can be found in grains such as rice and wheat, corn, and tubers such as potatoes, yams, cassava, starchy vegetables, and legumes. The starches in these foods do not easily dissolve in water. They are released and easier to be absorbed when they are cooked. These foods also need to go through digestion to release the energy molecules in them.
Some types of polysaccharides are not easily broken down during digestion. They are very helpful too, by providing the digestive system with roughage. Lettuce, whole grains, and bran are high in roughage, high in fiber, and are great in helping with food digestion.
It is important to choose healthy sources of carbohydrates than unhealthy sources. For example, whole grains, quinoa, beans, and unprocessed sources are better, as they are slow to digest and may reduce a person’s chances of weight gain, diabetes, and heart diseases.
What do carbohydrates do for the body?
Carbohydrates provide energy for the body. Each gram of carbohydrate provides 4 calories. Our bodies break carbohydrates down into glucose.
The cells in our bodies, tissues, and organs depend on glucose in the blood to function. Without it, the cells will eventually die. The liver and muscles use glucose all the time and can also store glucose for later use.
