- Ozone Depletion
Introduction: All about Ozone
 Like other environmental concerns, ozone depletion is an important issue and considered a major environmental issue by many environmental scientists.
Like other environmental concerns, ozone depletion is an important issue and considered a major environmental issue by many environmental scientists.
Have you ever felt the sun’s intensity ripping through your skin on a hot afternoon? Probably so.
But the sun is nowhere near the earth. The sun is estimated to be about 150 million kilometers (93 million miles) from our planet earth. Every day, as the sun rises, we begin to feel the heat. This heat is radiated through millions of space, and yet we still feel it.
The rays from the sun contain Ultra Violet Rays (UV Rays). UV rays are not all bad, because it helps humans with Vitamin D. But too much of it is very dangerous.
Manufacturing activities have caused a disturbance in the atmosphere’s natural balance since the industrial revolution. That has opened up the atmosphere for more UV rays to come through to the earth.
The Ozone Layer
It is a layer in the stratosphere containing a relatively high concentration of ozone gas.
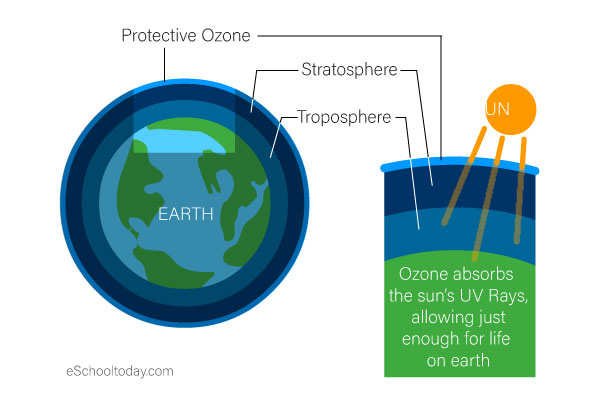 The earth’s atmosphere is divided into several layers, and each layer plays an important role. The first region extending about 10km upwards from the earth’s surface is called the troposphere. Many human activities like mountain climbing, gas balloons, and smaller aircraft operate within this region.
The earth’s atmosphere is divided into several layers, and each layer plays an important role. The first region extending about 10km upwards from the earth’s surface is called the troposphere. Many human activities like mountain climbing, gas balloons, and smaller aircraft operate within this region.
The next layer, extending about 15-60 km is called the stratosphere. The ozone layer is mainly found in the lower portion of the stratosphere from approximately 20 to 30 kilometers (12 to 19 mi) above Earth, though the thickness varies seasonally and geographically.
The ozone layer protects the earth from the sun’s UV Rays. If the ozone layer is depleted by human action, the effects on the planet could be catastrophic.
To better understand the Ozone Depletion problem, we first need to get a few terms right.
