- Clouds
Humidity, Relative Humidity, Adiabatic Cooling and Dewpoint
Here are four cloud formation terms to know.
Humidity
It is the amount of water in the air. The air in the atmosphere has water in it. At any temperature, one of the three states of water could be present. There could be water vapor (gas) if the temperature is very high. There could be tiny water droplets (liquid) if the temperature is at the dew point, or there could be ice crystals (solid) if the temperature is low. Air closer to the land surface usually contains water droplets because it is warmer than it is at higher altitude.
Relative Humidity
It is the ratio of the amount of moisture in the air to the amount it can hold at any given temperature. Let us say it is 90°F, and the Relative Humidity is 50%. That would mean that at 90°F, the air is holding half the amount of water it could hold at that temperature. If the Relative Humidity was 98%, it would mean that the air is holding almost all the moisture it could hold at that temperature. You can feel more moisture in the air when it is 90% than if it were 30%. Relative Humidity changes with temperature (that means it depends on the temperature)
Adiabatic Cooling
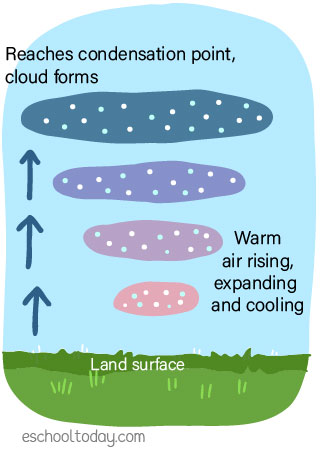 Anytime a block of air (called a parcel of air) is heated over the land surface, it begins to rise. As it rises and expands, its molecules spread out. As it continues to rise, it encounters decreasing atmospheric pressure, losing more heat. This cooling process is what we call ‘Adiabatic Cooling’. The reverse is ‘Adiabatic Heating’ where air descending through the atmosphere compresses with increasing pressure. Note that cooling by advection and radiation produces fog, frost, and dew, but clouds are formed by Adiabatic Cooling.
Anytime a block of air (called a parcel of air) is heated over the land surface, it begins to rise. As it rises and expands, its molecules spread out. As it continues to rise, it encounters decreasing atmospheric pressure, losing more heat. This cooling process is what we call ‘Adiabatic Cooling’. The reverse is ‘Adiabatic Heating’ where air descending through the atmosphere compresses with increasing pressure. Note that cooling by advection and radiation produces fog, frost, and dew, but clouds are formed by Adiabatic Cooling.
Dew point
It is the temperature at which Relative Humidity reaches 100%. It is the temperature at which water vapor in the air will reach saturation (turn to liquid form), assuming that the pressure and water vapor are constant. The dew point is not a fixed temperature because it can change with pressure and amount of water vapor. When the dew point temperature and air temperature are equal, the air is said to be saturated. Air temperature is never lower than the dew point. As soon as it gets lower, moisture is removed from the air in the form of condensation. At condensation, clouds and fog begin to form because the air is cooler than the dew point, and water vapor is turning into liquid.
