- Matter
Behavior of Matter
The particles in solids, liquids, and gases all behave in different ways but result similarly. They all expand when heated up.
Solids:
The particles in solids vibrate more and knock against each other when heated and result in taking up more space. The property of solids (metal) expansion makes it possible to join two metal pieces without welding.
See diagram below:
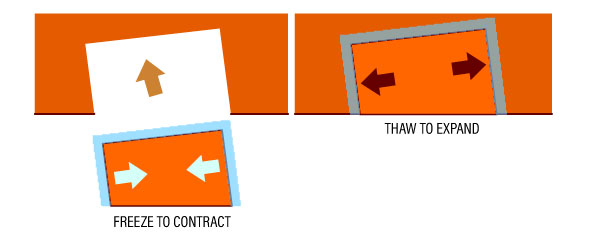
To join two metal pieces without welding, the smaller piece can be frozen to make it smaller. As the piece returns to normal temperature, it expands back and fits the space perfectly.
Liquids:
Particles in liquids move around each other some more, vibrate quickly, and also result in taking up more space.
Gases:
The particles in gases move freely in all directions and take up more room too. When heated, they move very quickly and move about more.
All three states result in taking up more room, also known as expansion. The expansion properties of solids, liquids, and gases have some advantages and disadvantages.
Here are a few:
One advantage of expanding metal is its use in thermometers. The mercury (liquid-metal) in the tube expands when they get hotter.
One disadvantage of expansion is that roads crack during the cold season because they contract and expand during the hot summer. This expansion can make road surfaces rough. Metal and steel structures used in bridges also expand when they heat up, causing fractures in the bridge.
