- Asexual Reproduction
Bulbs in vegetative propagation
Bulbs are shortened underground storage structures. They are stems that are enclosed with fleshy, concentric layered leaves. Bulbs produce smaller buds (lateral buds) that appear between the layers of the parent bulb. As the mature plant gets to the end of its life, the lateral bud develops into a smaller bulb that attaches to the base of the parent bulb. The new bulb can be separated and planted.
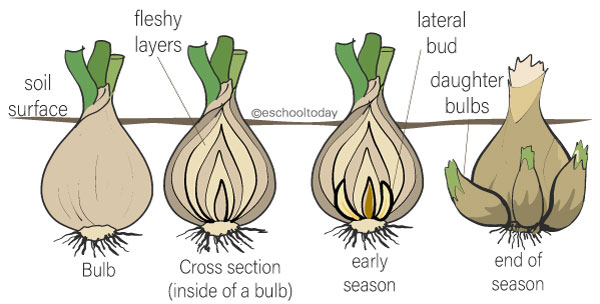
Examples include Tulips, Daffodils, Lilies, and onions.