- Asexual Reproduction
What is Vegetative Propagation?
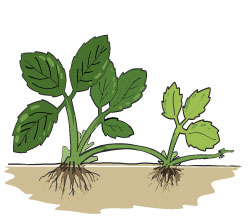
New plants can be produced from vegetative structures such as the roots, stems, and leaves of some plants. The process can be natural or artificial.
Roots:
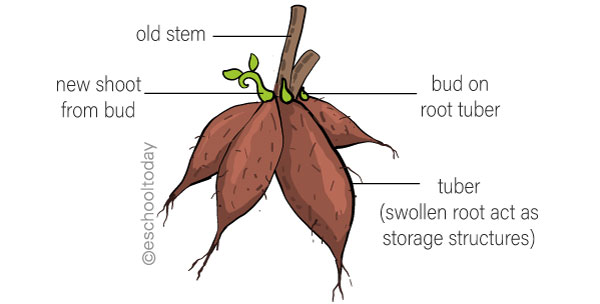
Some roots, such as those of sweet potato, begonia, and dahlia, have swollen roots that serve as storage structures. Tubers can develop into new plants that have identical genetic makeup as the parents. Tubers with buds at the base of the stems can also be separated and new plants produced from them.
Leaves:
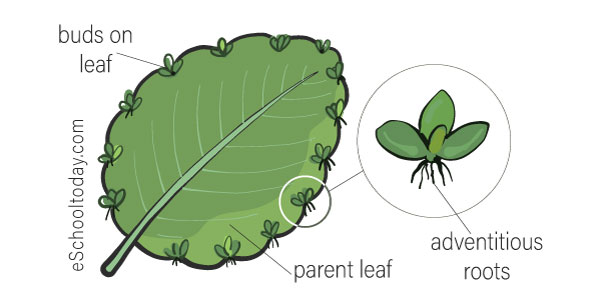
Some leaves, such as those of Begonia, have buds on their margins. These buds have adventitious roots. Usually, when such leaves touch the ground, new plants develop that grow into independent plants. They can also be cut and planted into new plants.
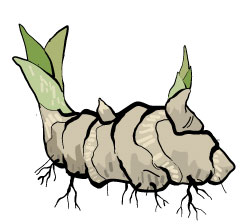
Stems:
In many plants, the stems have buds on them. Onions, daffodils, and strawberries have stems that can start new offsprings. Types of stems that can reproduce include
CLICK ON EACH STEM BELOW TO READ MORE!!