- Landforms
What is a Desert?
A desert is simply an arid land (too dry or barren to support vegetation) with very little rainfall. It is known that about a third of the earth’s land is made of deserts. Some natural features found on deserts include rock pedestals, desert pavements, and sand dunes.
Features of a desert include:
- Less than 10inches of rainfall per year
- Evaporation is more or equal to rainfall
- Has the sparse distribution of vegetation due to low moisture
- They usually have little cloud cover.
- Deserts may be cold or hot. Deserts close to the equator can have temperatures of over 38C (100F) and very cold nights.
The Great Sandy Desert and the Simpson Desert in Australia are good examples of hot deserts.
An example of a cold desert is The Patagonian Desert in Argentina, South America.
The Namib and Kalahari deserts of Southern Africa are also great examples of deserts with sand dunes up to about 300m high.
One way that desert forms is when rain clouds are moved by the wind into very high mountains. Condensation occurs and, rain is forced down on that side of the mountain, leaving the other side dry. The dry side of the slope now becomes the rain shadow with very little humidity.
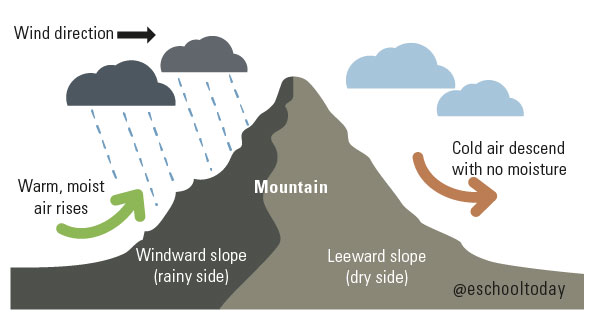
The great Gobi desert in India is known to have been created in this way, when clouds and winds move up the Himalayas Mountains and deposit rain, leaving the other side of the mountains very dry.
